Tert-Butyl Chloroacetate: Critical Role in Modern Chemistry and Industry
Historical Development
Chemistry keeps changing, but a handful of molecules keep popping up decade after decade because of what they can do in the lab and in the factory. Tert-butyl chloroacetate traces its roots back through the mid-20th century, surfacing as research intensified on organic esters and synthetic pathways for pharmaceuticals. Early on, chemists valued it for its ease in participating in alkylation and acylation reactions, so it earned a place among versatile building blocks. Back in the day, not many alternatives existed for protecting functional groups during synthesis or for introducing alkoxy carbonyl units. Today, its development benefits enormously from the careful refinement of esterification and halogenation methods, bearing the marks of dedicated researchers who chased both efficiency and cleaner reactions long before “green chemistry” hit the mainstream.
Product Overview
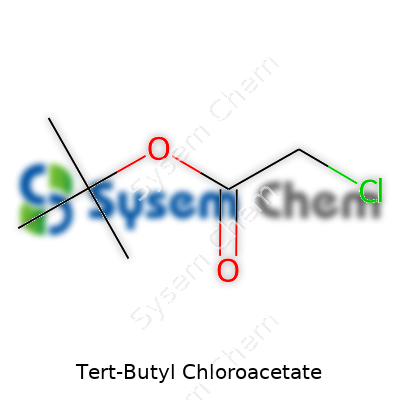
Tert-butyl chloroacetate belongs to the ester family and carries a chloroacetate group attached to a tert-butyl moiety. This compound looks clear and carries a faint sweet scent—less aggressive than some smaller molecule esters, yet it hints at something you wouldn’t want lingering in the air. Most often, chemists pick it up as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, or novel materials. Across many shelves, professionals know they’re handling something with a stable core that responds well to nucleophilic substitution ceremonies in the flask.
Physical and Chemical Properties
This liquid holds a boiling point hovering near 155°C and weighs in at a modest density just under 1 g/cm³. The molecular formula, C6H11ClO2, packs a polar chloro group, lending reactivity to a backbone that doesn’t easily oxidize or break down at room temperature. Solubility paints an interesting picture—tert-butyl chloroacetate shows low solubility in water but mixes easily with common organic solvents, especially ethers and aromatic hydrocarbons. This trait aids separation and work-up steps in multi-step syntheses, making it an approachable choice in both research and production shops.
Technical Specifications and Labeling
Bottles and drums come stamped with their identity, purity grade, and batch number. Reputable suppliers aim for purity above 98%, limiting moisture and acid impurities to protect its shelf life. Labels wear hazard symbols for “Harmful” and “Irritant,” and shipping boxes carry signatures from regulatory bodies like the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. Anyone using this chemical expects a technical sheet to spell out specific gravity, refractive index, and standards for trace impurities—this information builds trust in every transfer and reaction.
Preparation Method
Synthesizing tert-butyl chloroacetate starts with the classic Fischer esterification, blending tert-butanol and chloroacetic acid in the presence of acid catalysts. In my experience, this step works well under reflux with sulfuric acid or p-toluenesulfonic acid. Tech-forward operations sometimes favor phase-transfer catalysis to speed up rates and boost yields. Afterward, distillation clears out by-products and leaves a clear, pungent ester ready for the next transformation. Each lab finds its own rhythm, tweaking solvent choices and catalyst loading to balance safety, scalability, and environmental cost.
Chemical Reactions and Modifications
Among chemists, tert-butyl chloroacetate plays the role of both participant and spectator in key transformations. Nucleophilic substitution stands at the center, where nucleophiles like amines, alcohols, and thiols displace the chlorine atom, creating libraries of derivatives optimal for downstream applications. I’ve watched it transform into protected amino acids, tricky ligands, or even advanced intermediates for specialty polymers. Its tert-butyl group sometimes comes off under acidic conditions, freeing a carboxyl group for more chemistry. Anyone well-versed in acylations and alkylations spots tert-butyl chloroacetate not just as a solvent-filler but as a cornerstone for creative synthesis.
Synonyms and Product Names
Chemicals often go by more names than close friends at a wedding. Tert-butyl chloroacetate, or tert-butyl 2-chloroacetate, crops up as Chloroacetic acid tert-butyl ester and 2-chloroacetic acid tert-butyl ester on certificates of analysis. European suppliers sometimes shorten it to TBCAC. CAS number 107-59-5 follows it everywhere, helping trace orders and search regulatory records without confusion.
Safety and Operational Standards
Safety tops every priority list in facilities using tert-butyl chloroacetate. Vapors irritate the eyes and lungs; skin exposure can bring stinging, redness, and longer-term sensitization in some workers. I always suit up with nitrile gloves, splash goggles, and lab coats, making sure spill kits stay within reach. Proper ventilation—never an afterthought—prevents vapor buildup during weighing and mixing. Laboratories fix strict storage norms: cool, dry shelves away from heat sources and oxidizers. Data sheets require regular updating, especially when handling larger volumes or integrating automation. Emergency plans focus on neutralizing spills with sodium bicarbonate and rinsing with copious water—quick response marks the line between a minor mishap and an incident.
Application Area
The usefulness of tert-butyl chloroacetate cuts across industries. Drug designers view it as a neat building block for synthesizing beta-lactam antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and select anti-cancer agents. Crop scientists lean on it for developing herbicide and fungicide precursors, aiming to boost selectivity and environmental break down. Specialty material labs use it to introduce new functionalities in photoresists and elastomers. In my own work, it enabled protection strategies that would have otherwise demanded difficult, expensive routes.
Research and Development
Progress centers around greener, more efficient routes for both producing and modifying tert-butyl chloroacetate. Catalysis groups examine new acids and bases for lowering activation barriers. Teams in process chemistry hunt for ways to recycle solvents and cut waste. Applications grow with each advance—bioconjugation and click chemistry see derivatives featured in cutting-edge protocols. Proprietary routes for safer handling and inline purification spark collaboration between industry and academia, mixing discovery with practical innovation. The research journals fill up with reports of new analogs, reaction cascades, and bioactive molecules—spurred by the flexibility of the chloroacetate motif.
Toxicity Research
With use comes responsibility. Researchers invest long hours studying how tert-butyl chloroacetate interacts with biological systems. Acute inhalation and dermal contact cause irritation, and animal studies track dose-dependent responses to map thresholds for harm. Data feeds regulation—workplace exposure limits come from this steady stream of research. Environmental assessments identify breakdown pathways in soil and water, looking for products that degrade quickly without mounting up in plants or wildlife. I’ve seen more demand for analytical methods with higher sensitivity as society keeps cracking down on trace contaminants and demanding cleaner water and air.
Future Prospects
Tert-butyl chloroacetate stands poised to stay relevant as science pushes boundaries. Ongoing projects focus on engineering new derivatives to unlock untapped medical therapies and smarter crop protection. Sustainable routes—catalyst alternatives, solvent recycling, process intensification—promise to trim the ecological footprint. Increasing automation in chemical manufacturing will tighten safety standards, lowering risk for both operators and communities nearby. Training the next generation of chemists means passing down respect for reagents like this, along with the knowledge to harness their power thoughtfully. Fields like bioorthogonal chemistry and molecular imaging could find unexpected uses for this ester, drawing together decades of craftsmanship, careful record-keeping, and a willingness to try something new.
Understanding the Role in Chemistry Labs
Tert-butyl chloroacetate doesn’t grab headlines like new medicines or battery tech, but in a chemist’s toolkit, it deserves some spotlight. Its main job: helping build more complicated molecules. Drug companies reach for compounds like this when sketching out new treatments, often as a starting block for molecules that may lead to breakthroughs. This work isn’t about mixing household cleaners; the stakes involve tight regulations, lots of trial and error, and a tight focus on safety.
Molecular Building in Pharma and Beyond
Most of what makes this chemical valuable comes down to building blocks. Medications often need backbone structures with precise bits attached. Tert-butyl chloroacetate offers up a chloroacetyl group—sort of like a high-energy Lego for organic chemists. It lets scientists bolt it onto a molecule, then swap or reshape other pieces later. For example, research covering antiviral and anticancer drugs includes steps where this compound comes into play, connecting and reshaping carbon atoms with functional groups that determine how the final product works in the body.
The agricultural field doesn’t ignore these tools either. Herbicides and insecticides sometimes need tweaks so they last longer in crops or break down at the right speed. The chemical steps involved often use tert-butyl chloroacetate to attach new features during the development process—usually aiming for results that either break down with less residue or ward off tougher pests. Chemical patents over the past decade show a steady stream of inventions where this little ester appears.
Why Its Use Matters for Safety
A lot of these specialty reagents don’t wind up in your medicine cabinet or kitchen shelf. Their value shows up in how safely, quickly, and cleanly they turn into something else. Like many chemicals carrying “chloro” in their names, tert-butyl chloroacetate raises real safety questions. Breathing vapor or spilling it on skin brings health risks, from skin burns to possible organ damage. That’s something early chemists didn’t always appreciate, and some accidents in the past forced labs to rethink how they handle chemicals like this one. Published safety data show plenty of short- and long-term risks if people don’t take the right precautions.
Factories and labs have learned lessons after decades at the bench. Strong gloves, fume hoods, eye protection, and automated systems keep accidents way down. Researchers focus more on reactions that limit hazardous byproducts, turning to greener chemistry routes that avoid chlorine-based waste as much as possible. Still, every step involving tert-butyl chloroacetate draws scrutiny from safety officers and environmental regulators, partly because spilled material or airborne vapors don’t just disappear harmlessly.
The Road Toward Safer and Greener Chemistry
Not every process can ditch hazardous ingredients yet, so most companies work on containment and cleanup. Innovative chemists keep experimenting with alternative reagents; some teams focus on swapping out this type of ester for biodegradable or less toxic stand-ins when possible. Universities and industry labs publish new reaction methods that cut waste or use renewable solvents. Pressure from investors, regulators, and employees has shifted company goals toward lowering their “toxic footprint.”
As the world keeps demanding cleaner factories and safer labs, tert-butyl chloroacetate represents more than a mere ingredient—it shows how science has to juggle progress, profit, and responsibility. Every shift toward greener chemistry owes something to innovators wrestling with chemicals just like this, improving old recipes so tomorrow’s risks shrink without slowing down discovery.
Why Storage Really Matters
Anyone who has spent time in a chemical lab understands the stress that comes from opening a storage cabinet and wondering whether anything changed overnight. Chemicals each have their mood swings, and from my experience, even substances that seem stable can behave unpredictably over time. Tert-Butyl Chloroacetate shows the kind of reactivity that has taught many chemists—including me—the value of respecting proper storage procedures. One wrong move can mean ruined research or, worse, a safety issue that nobody wants to deal with during a late-night experiment.
Key Storage Requirements
You won’t keep Tert-Butyl Chloroacetate safe just by putting it on any shelf. This compound needs a dry, tightly closed container because any contact with moisture can trigger slow hydrolysis or even cause it to degrade. Water in the air loves to find its way inside, little by little, especially if the cap isn’t on right. Here’s what I’ve learned: make a habit of double-checking the seal after every use. Too many people forget, and whatever’s in the bottle slowly turns useless or even hazardous.
Cool and stable temperatures help prevent unwanted reactions. I never keep this chemical near sunlight or heat sources. A shaded spot below 25°C (room temperature works well during most months) offers enough reassurance, but I add a thermometer nearby just to monitor for those steamy summer spikes. Changes in temperature can hurt shelf life and bump up the risk of pressure build-up inside the container.
Ventilation and Incompatibility
If you store Tert-Butyl Chloroacetate, choose a spot with proper air circulation. Vapors build up fast in small spaces, and I’ve seen even small leaks lead to headaches—literally and figuratively. Rely on a ventilated cabinet whenever possible. Store this chemical away from strong bases, oxidizers, or acids because things might get ugly if there’s ever a spill.
Flammable solvents often crowd the shelves of every stockroom, but this chemical does not pair well with them. I label my shelves and encourage coworkers to create clear separation. It takes a few extra steps during inventory checks, but this upfront effort saves time during emergencies and reduces cleanup after inevitable drips or accidents.
Labeling and Documentation
Trusting your memory rarely works. Proper labeling, with exact dates and clear hazard warnings, makes a difference. Audits always find bottles that have lost their labels or faded beyond recognition, and nobody wants to question what’s inside during a crisis. Being thorough on day one prevents mishaps six months down the road. I jot everything in a logbook too, tracking when to check or replace older stock before trouble starts.
Chemical Safety Isn’t Optional
I’ve lost track of how many training sessions have stressed the same message: treat every chemical with respect, even ones that seem harmless at first glance. Wear gloves, goggles, and protect skin from splashes. Nobody regrets over-preparing in the lab but many regret the opposite. Eye-wash stations and spill kits stay close at hand. Practicing these habits makes emergencies rare.
Building Lasting Habits
Safe storage turns into second nature once you set smart systems and stick to them. Chemical stewardship goes beyond simple compliance—it safeguards research, reputations, and well-being. I’ve learned from mentors, mistakes, and moments of luck. Follow the basics, double-check your work, and encourage a culture where safe storage earns respect every single day.
Understanding the Substance
Tert-butyl chloroacetate pops up in a range of labs and workshops. Chemists rely on it for synthesizing specialty compounds. This chemical doesn’t make headlines like pesticides or cleaning agents, but it deserves a close look for what it brings to the workbench—and the risks lurking with its use.
Hazards Worth Noting
The smell from compounds like tert-butyl chloroacetate often gives away their energy level. Their vapors sting. This one isn’t any different. If a drop lands on your skin, it can burn. A spill gets noticed right away because it irritates the eyes. Inhaling the vapors means you’re coughing and your throat feels raw. These are not nuisance effects. The irritation here is not just discomfort, it’s your body signaling danger.
Reports show it damages living tissue. The skin loses layers after exposure; eyes can take a hit that leads to real injury. Inhalation triggers the sort of cough that keeps you up all night, sometimes leading to worse problems if you can’t access clean air. Swallowing it leads straight to nausea and vomiting—no mystery about what your body thinks of this compound coming in contact with it.
What the Science Says
Chemists don’t guess about toxicity. They run tests. Studies prove this is more than a mild irritant. Tert-butyl chloroacetate contains a reactive chloro group, making it a solid alkylating agent—chemically aggressive. Effects such as burns and respiratory distress make sense, given its structure and action. The EPA labels similar compounds hazardous waste, reflecting both the dangers during use and the problems with disposal.
A person doesn’t need a chemistry degree to make sense of the Material Safety Data Sheet: keep it off your skin and out of your lungs. Anyone handling it should wear gloves, goggles, and work under a vented hood. Even splash-proof lab coats serve a real purpose here. These steps aren’t overkill—they’re standard because they work.
Personal Experience in the Lab
Years spent in university labs teach a thing or two very quickly. One of my colleagues skipped gloves once while transferring tert-butyl chloroacetate. A small drop landed on a finger, and within a minute redness appeared. Washing under cold water helped only a bit. She ended up seeking medical attention, learning the hard way it’s not only about safety policy—it’s about long-term health. The scar faded, but she keeps a pair of heavy-duty gloves close now, a personal reminder.
Stories like this pass through every lab. There’s no substitute for experience in handling chemicals, and while even experts slip sometimes, proper habits make a difference over a career. Chemical burns and lung irritation don’t care if you’re a beginner or a seasoned researcher.
Finding Real Solutions
Knowledge goes a long way in managing risks. Universities and companies step up training to keep young chemists safe. More facilities now install air monitors and quick safety showers. Labels have grown clearer. Chemistry suppliers publish better guides, spelling out not just what chemicals do, but how they behave if something goes wrong. Waste handling receives greater attention now, keeping hazardous leftovers out of water supplies.
Hazardous chemicals like tert-butyl chloroacetate aren’t going away. The world depends on lab research to fuel medicine, technology, and innovation. By sticking to clear controls—proper safety gear, honest training, and vigilant procedures—the risks become manageable. Respect for these substances often comes from hard lessons, but smarter habits mean fewer injuries, less regret, and science that moves ahead without costing someone their well-being.
Understanding the Basics
Tert-butyl chloroacetate sounds pretty technical, but it fits right into the toolkit of organic chemists. The chemical formula is C6H11ClO2, which tells you a lot about what’s inside this compound. Six carbons, eleven hydrogens, one chlorine, and two oxygens: each element plays its own role, guiding this molecule’s behavior in reactions. If you’re mapping out reaction pathways, this information turns into your foundation.
Breaking Down Its Molecular Weight
The molecular weight of tert-butyl chloroacetate is about 150.6 g/mol. This figure isn’t just a number from a textbook. It anchors the way chemists prepare reagents and calculate yields. Weighing out 150.6 grams of it means you have a mole on the scale, ready to react. I remember more than a few late nights in the lab double-checking these weights before setting up reactions, because getting it wrong throws off everything down the line.
Real-World Value in Synthesis
This molecule finds real purpose as a building block for more complex molecules. Its tert-butyl group offers some steric bulk, and the chloroacetate part acts as a key player in substitution reactions. In my own work with drug discovery projects, tert-butyl chloroacetate came up as a starting point for creating intermediates. The chlorine atom is reactive: it’s eager to swap places with nucleophiles, so it doesn’t just sit back. I’ve watched fellow chemists favor it for its clean and predictable behavior in substitution reactions, saving hours of trouble compared to less cooperative reagents.
Handling and Safety Concerns
Working with organochlorine compounds calls for a bit of respect and some common sense. Tert-butyl chloroacetate, with its volatile nature and sensitivity to moisture, reminds you to reach for the right gloves, goggles, and fume hood every time. Safety is never just a checklist in a lab — I’ve seen close calls turn into learning moments simply because someone took shortcuts in ventilation or ignored a spill.
Risks and Responsible Use
Beyond the lab, chemicals like this one sometimes end up in the wrong hands or cause harm through carelessness. Regulatory bodies like OSHA set clear guidelines for safe handling and disposal. In my years watching new researchers join the lab, a good mentor always returns to this topic: proper labeling, secure storage, clear training. We all want to keep our workplace safe, and ignoring small details can have big consequences.
Looking Ahead: Smarter Chemistry
Advances in chemistry are driving a push for greener manufacturing and safer reagents. Even though tert-butyl chloroacetate has carved out a niche, research aims to minimize hazardous byproducts and find environmentally friendlier alternatives. Solvent choice and reaction conditions make a major difference. I’ve seen projects succeed just by swapping out the solvent or optimizing a step to use less material, cutting both cost and waste.
Getting to know the nuts and bolts of tert-butyl chloroacetate means more than memorizing its formula or weight. Anyone working with it carries a responsibility to accuracy, safety, and the future of chemical research.
Recognizing the Risks
Tert-Butyl chloroacetate stands out among reagents because it packs a punch on both the health and chemical sides. Many folks in the lab remember the first time a senior reminded them never to underestimate even the “easier” esters. This compound deserves respect. On skin, it can irritate deeply. Vapors find their way into lungs, leaving a scratchy, burning sensation. One lab accident in grad school ended with a classmate scrubbing furiously under the safety shower after an unnoticed splash. Tert-butyl chloroacetate taught all of us that skipping goggles or gloves doesn’t pay off.
Personal Protective Equipment is Non-Negotiable
Goggles, nitrile gloves, and a solid lab coat serve more than just to tick a checklist—they put a key barrier between the chemist and a nasty acid chloride. Splatters jump farther than expected, especially when handling bottles or transferring liquids. I’ve watched a seasoned postdoc don a face shield after a drop bounced off glassware and landed millimeters from an eye. The close call drove home that even short tasks deserve all the proper gear.
Ventilation and Engineering Controls
Fume hoods turn a risky procedure into a manageable one. No matter how tempted people get to handle quick transfers on the open bench, the volatile nature of tert-butyl chloroacetate shifts those risks upward. Inhaling even brief fumes leaves a bitter taste and a cough that lingers. Reliable fume extraction isn’t just about comfort. OSHA chemical hygiene guidelines spell it out clearly: volatile chemicals ask for real ventilation. No shortcut beats working with sash down and airflow checked.
Storing Smart Prevents Bigger Headaches
This chemical wants to rest in a cool, dry cabinet, away from acids and bases. I once opened a crowded flammables locker to a whiff of sharp, strange odor. It turned out the tert-butyl chloroacetate container sat next to an unlabeled bottle of ammonia solution. Even sealed tight, a minor leak spells trouble if incompatible reagents mingle. Chemical inventory lists updated regularly keep everyone from guessing; easy-to-read hazard signs on the doors back that up.
Spill Response Knows No Weekends
A spilled splash on a Friday afternoon still demands immediate cleanup. Neutralizing materials—like sodium bicarbonate for acids—live near the bench for a reason. I keep a small spill kit handy; gloves, goggles, and an unopened box of absorbent pads make life easier during those rushed moments. Training can’t rely on a single annual refresher. Walking through cleanup steps every few months matters. Everyone from interns to old-timers needs muscle memory so panic doesn’t take over.
Waste Disposal: No Corners Cut
Pouring even a few milliliters down the drain risks both personal and environmental harm. Proper waste collection containers, clearly labeled, keep accidents low. A university ran a spot-check once, finding that incorrect segregation nearly caused a dangerous reaction. Waste management teams count on honesty and clarity from each bench chemist. Cutting corners here only brings headaches later.
Building Safety into Daily Routines
I always stress that safe habits start with small steps. Tert-butyl chloroacetate isn’t unique in needing careful handling, but it offers a potent reminder that disaster rarely happens from big blunders—it’s the cut corners that catch up with us. Real expertise means treating these tasks with humility and attention each and every time.